An addition polymer consists of two different kinds of monomers. The monomers that form condensation polymers are di- or polyfunctional.
Difference Between Addition Polymerisation And Condensation Polymerisation Process Features Type Of Polymers Produced Examples
Condensation polymerizations often but not always combine two different monomers in an alternating structure.

. A condensation polymer is formed when monomers bond to each other without the loss of atoms. Addition polymerisation produces addition polymers through the addition of olefinic monomers without the formation of any by-product. Condensation polymers loose watermolecules during polymerisation whereas Addition Polymers do not.
Addition and condensation polymers. Examples include polyester polyamide polyurethane and polysiloxane. A condensation polymer is formed when monomers bond to each other without the loss of atoms.
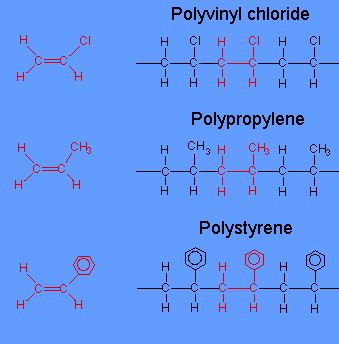
The very small molecule produced in the condensation can be H 2 O HCl or some other simple molecule. From this table it must be quite obvious that the main difference between both addition and condensation polymerization is that in the case of addition polymerization the polymers are formed through the addition of monomers. Addition polymers include polystyrene polyethylene polyacrylates and methacrylates.
A condensation polymer is made of only one kind of monomer. The difference between addition and condensation polymerization is that for addition polymerization monomer should be an unsaturated molecule whereas for condensation polymerization. However in a condensation reaction there is a loss of a molecule of water ammonia etc.
A small molecule such as water is produced when the monomers react to build the polymer. A polymer can grow from any location on the chain where a functional group is available. A condensation polymer consists.
In contrast condensation polymerisation produces condensation polymers through the intermolecular condensation of two different monomers with the formation of small molecules such as HCl water ammonia etc. Where as condensation polymerization involves individual chemical reactions between pairs of reactive monomers. There are two types of polymers.
Polyethylene PE polyvinyl chlori. Polymers usually grow by C-O or C-N bond formation. A large number of monomers combine with the loss of simple molecules water ammonia HCl alcohol to form a polymer having molecular formula of the repeating unit.
An addition polymer is made of only one kind of. The main difference between addition and condensation polymerization is that in addition polymerization the polymers are formed by the addition of monomers with no by-products whereas in condensation polymerization the polymers are formed due to the condensation of more than one different monomers resulting in the formation of small. Additional polymerization involves polymers which are formed by the combination of alkene monomers to produce a single huge molecule only.
An addition polymer consists of two different kinds of monomers. A condensation polymer is made of only one kind of monomer. The main difference between addition and condensation polymerization is that in addition polymerization the polymers are formed by the addition of monomers with no by-products whereas in condensation polymerization the polymers are formed due to the condensation more than one different monomers resulting in the formation of small molecules such as HCl.
An addition polymer is made of only one kind of monomer. Condensation polymers are formed by the reaction of bi- or polyfunctional molecules with the elimination of some small molecule such as water as a by-product. This is part of the HSC Chemistry course under the topic Polymers.
Condensation polymerization is a slower process than addition polymerization. A condensation polymer is formed when monomers bond to each other without the loss of atoms. Addition and condensation polymerization are the two major processes of producing a polymer compound.
An addition polymer is made when the monomers lose an atom or group of atoms while forming the polymer. Condensation polymerization involves polymers which are formed by the combination of monomers with the elimination of simple molecules like water H 2 O or ammonia NH 3. There are many differences between the two processes.
That is an ester or amide linkage forms. An addition polymer is made when the monomers lose an atom or group of atoms while forming the polymer. Nylon6-6 is the most common polyamide which is obtained by heating hexamethylene diamine with adipic acid under N 2 at.
14 rows Addition polymerisation results in the formation of addition polymers whereas condensation. Typical examples of such polymers are Polyesters and Polyamides. The most important distinction is that in addition to polymers there is no loss of atom.
1483 Explain the differences between addition and condensation polymerisation. Addition polymerization leads to homo-chain polymers whereas condensation polymerization leads to hetero-chain polymers. Condensation Polymerization involves polymers which are formed by the combination of monomers with the elimination of simple molecules like H 2O or N H 3.
HSC Chemistry Syllabus model and compare the structure properties and uses of addition polymers of ethylene and related monomers for example. An addition polymer consists of two different kinds of monomers. A polymer does not contain all the atoms originally in the monomer units.
To understand the difference between addition and condensation Polymerization one must be familiar with the basic difference of an addition and condensation Polymerization that is in addition Polymerization the polymers are formed by the addition of monomers with no by-products whereas in condensation Polymerization the polymers are formed by the. Different monomers add to form a polymer with same molecular formula of the repeating structural unit as that of starting monomer. The main difference between addition and condensation polymerization is that in addition polymerization the polymers are formed by the addition of monomers with no by-products while in condensation polymerization polymers are formed due to the condensation of two different monomers resulting in the formation of small Click to see full answer.
Addition polymerization involves a rapid chain reaction of activated monomers by addition reaction.
12 Difference Between Additional And Condensation Polymerization With Examples Viva Differences

Addition Polymerization And Condensation Polymerization Hindi Youtube

Difference Between Addition Polymerization And Condensation Polymerization Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Difference Between Addition Polymerization And Condensation Polymerization Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
0 Comments